You might think bamboo clothing is an eco-friendly choice because bamboo grows quickly and requires fewer resources than other crops. While this is true, the environmental impact of bamboo depends on how it is farmed and processed. For example, some bamboo plantations absorb up to 12 tons of carbon dioxide per hectare annually, but intensive farming can harm biodiversity by replacing mixed forests with monocultures. Additionally, bamboo is often harvested before it reaches its full carbon storage potential, prioritizing yield over sustainability. These factors make the environmental benefits of bamboo clothing more complex than they first appear.
Key Takeaways
- Bamboo grows fast and needs fewer resources, so it’s renewable.
- Bamboo clothes can be better than cotton since they need less water and no pesticides.
- Making bamboo viscose can hurt nature because of harmful chemicals. Look for safer ways of processing.
- Labels like OEKO-TEX and FSC show if bamboo clothes are eco-friendly and responsibly made.
- Picking brands that are honest and care about the planet helps the environment.
Benefits of bamboo clothing

Bamboo as a renewable resource
Fast growth and minimal resource requirements
Bamboo is one of the fastest-growing plants on Earth. Some species can grow over three feet in a single day. This rapid growth makes bamboo a highly renewable resource. Unlike trees, which take decades to mature, bamboo can be harvested within three to five years. Its ability to regenerate quickly after harvesting reduces the need for replanting, making it an efficient and sustainable option for clothing production.
Bamboo also thrives in poor soil conditions and requires minimal resources to grow. It does not demand extensive irrigation or chemical inputs, which helps preserve the environment. According to the Green Initiative, bamboo’s rapid growth and sustainable harvesting practices enhance its environmental benefits, especially when compared to slower-growing plants like cotton.
Ability to grow without pesticides or fertilizers
Bamboo naturally resists pests and diseases, eliminating the need for harmful pesticides. This quality protects surrounding ecosystems from chemical contamination. Additionally, bamboo grows well without synthetic fertilizers, which reduces the risk of soil and water pollution. The Roundup highlights that bamboo’s ability to grow without chemicals makes it a more sustainable choice than conventional cotton.
Water efficiency
Bamboo’s low water needs compared to cotton
Bamboo requires significantly less water than cotton. While cotton farming often relies on irrigation, bamboo grows using only natural rainfall. A comparison of water usage shows that bamboo’s water needs are minimal, whereas cotton farming is highly water-intensive. This efficiency makes bamboo a more sustainable option, especially in regions facing water scarcity.
Thrives in diverse climates, reducing strain on resources
Bamboo can grow in a variety of climates, from tropical to temperate regions. Its adaptability reduces the strain on local resources and allows it to thrive in areas unsuitable for other crops. This versatility supports sustainable farming practices and helps reduce the environmental footprint of bamboo clothing.
Carbon absorption
Bamboo’s role in carbon sequestration
Bamboo plays a significant role in absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Studies show that bamboo forests can fix large amounts of carbon, making them valuable for combating climate change. For example, Moso bamboo, commonly used in textiles, contributes to carbon storage while also stabilizing soil and preventing erosion.
Contribution to mitigating climate change
By absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen, bamboo helps mitigate the effects of climate change. Its rapid growth allows it to sequester carbon more quickly than many tree species. According to research by Wang et al. (2013), bamboo forests in China store significant amounts of carbon, highlighting their ecological importance. When used in durable products like bamboo clothing, the carbon remains stored for longer periods, further enhancing its environmental benefits.
Environmental concerns in bamboo clothing production
Chemical-intensive processes
Issues with viscose production and toxic chemicals
The production of bamboo viscose involves harsh chemicals that harm the environment. Manufacturers use substances like carbon disulfide, caustic soda, and sulfuric acid to break down bamboo into a usable fiber. These chemicals are toxic and can cause significant environmental damage if not handled properly. For example, over 50% of the chemicals used in viscose production often escape into the environment, contaminating water sources and harming ecosystems.
| Chemical Process | Chemicals Used | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Bamboo Viscose Production | Caustic Soda, Carbon Disulfide | Highly toxic, significant environmental concerns |
| Viscose Production | Sodium Hydroxide, Carbon Disulfide | Serious health issues, environmental damage |
Impact on workers and ecosystems
The use of toxic chemicals in bamboo clothing production also affects workers. Exposure to carbon disulfide can lead to severe health problems, including nerve damage. Additionally, ecosystems near production facilities suffer from chemical runoff, which disrupts aquatic life and pollutes soil. These issues highlight the need for safer production methods.
Energy consumption
High energy requirements in manufacturing
Producing bamboo clothing requires significant energy, especially during the chemical processing stages. Factories often rely on energy-intensive machinery to transform raw bamboo into fabric. This high energy demand increases the carbon footprint of bamboo clothing, making it less sustainable than it appears.
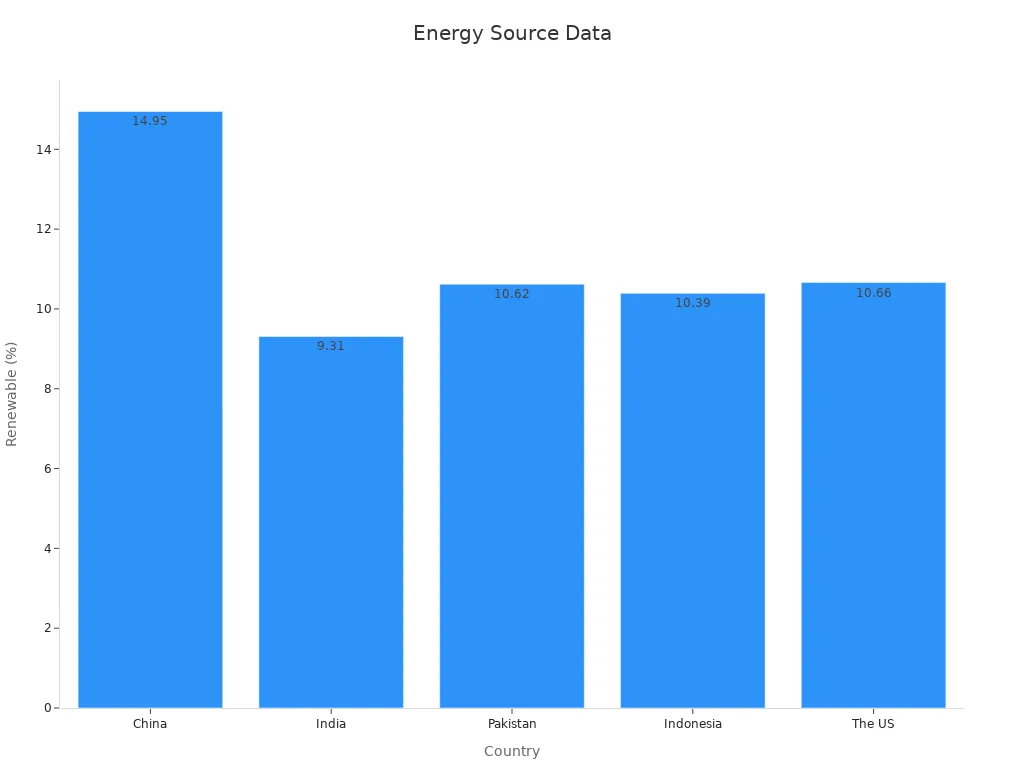
Reliance on non-renewable energy sources
Many countries producing bamboo clothing depend heavily on non-renewable energy. For instance, China, a major producer, generates only 14.95% of its energy from renewable sources. This reliance on fossil fuels contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, further impacting the environment.
Waste management challenges
Risks of improper disposal of chemical waste
The viscose production process generates large amounts of hazardous waste. Improper disposal of these chemicals, such as caustic soda and carbon disulfide, poses significant risks to the environment. Toxic discharges often end up in rivers and lakes, affecting water quality and aquatic ecosystems.
Importance of sustainable waste practices
Adopting sustainable waste management practices can reduce the environmental impact of bamboo clothing. Recycling and capturing chemicals during production can prevent harmful discharges. However, many factories lack the infrastructure to implement these practices, making it essential for consumers to support brands that prioritize sustainability.
Bamboo clothing vs. other fabrics
Bamboo vs. cotton
Water and pesticide use in cotton cultivation
Cotton farming consumes vast amounts of water and relies heavily on pesticides. Producing just one cotton T-shirt can use over 2,700 liters of water. This water-intensive process strains resources, especially in regions already facing drought. Additionally, cotton farming uses 16% of the world’s pesticides, which harm soil, water, and wildlife. These chemicals also pose health risks to farmers and nearby communities.
Organic cotton as a sustainable alternative
Organic cotton offers a more sustainable option. It avoids synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, reducing environmental harm. Organic farming also uses less water by relying on rain-fed systems. However, organic cotton still requires more water than bamboo clothing, making bamboo a better choice in water-scarce areas.
Bamboo vs. polyester
Polyester’s fossil fuel origins and microplastic pollution
Polyester, a synthetic fabric, comes from petroleum, a non-renewable resource. Its production emits significant greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change. Washing polyester garments releases microplastics into waterways, harming marine life. These microplastics persist in the environment for centuries, creating long-term pollution.
Bamboo’s renewable nature but chemical concerns
Bamboo clothing comes from a renewable plant, making it more eco-friendly than polyester. However, the chemical-intensive viscose process raises concerns. Choosing bamboo processed through sustainable methods, like the lyocell process, minimizes these issues and makes it a greener alternative.
Bamboo vs. other eco-friendly fabrics
Comparing bamboo to hemp and lyocell
Hemp and lyocell are two other eco-friendly fabrics. Hemp grows quickly, like bamboo, and requires minimal water and no pesticides. Lyocell, made from wood pulp, uses a closed-loop process that recycles chemicals, reducing waste. Both fabrics have lower environmental impacts than chemically processed bamboo.
Advantages of bamboo processed using the lyocell method
When bamboo is processed using the lyocell method, it becomes a strong competitor to hemp and lyocell. This method avoids harmful chemicals and ensures a closed-loop system. Bamboo processed this way retains its renewable benefits while reducing its environmental footprint.
Sustainable bamboo clothing options

Eco-friendly production methods
Lyocell process and its benefits
The lyocell process offers a more sustainable way to produce bamboo clothing. It uses a non-toxic amine oxide to dissolve bamboo fibers, avoiding harmful chemicals like sodium hydroxide. This method operates in a closed-loop system, reusing 99.5% of the chemicals, which minimizes waste and pollution. Products made through this process often receive Oeko-Tex 100 certification, ensuring they are safe for human use. By choosing bamboo clothing made with the lyocell process, you support a cleaner and more efficient production method.
Bamboo linen as a less chemically intensive option
Bamboo linen provides another eco-friendly alternative. This method mechanically processes bamboo without using harsh chemicals. Although it requires more labor, it produces a soft and durable fabric. Bamboo linen retains the plant’s natural benefits, such as its rapid growth and low water needs. By opting for bamboo linen, you can enjoy sustainable clothing that aligns with environmentally conscious values.
Certifications to look for
Importance of OEKO-TEX and FSC labels
Certifications like OEKO-TEX and FSC help you identify sustainable bamboo clothing. OEKO-TEX Standard 100 ensures that textiles are free from harmful substances, while FSC (Forest Stewardship Council) guarantees that bamboo is sourced responsibly. These labels provide assurance that the clothing meets high environmental and safety standards.
Indicators of responsible sourcing and manufacturing
Other certifications also highlight eco-friendly practices. For example:
| Certification Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Made in Green by Oeko-Tex® | Combines safety and sustainability standards for textiles. |
| Global Organic Textile Standard | Requires organic fibers and strict environmental criteria for processing. |
| Cradle2Cradle Certification | Evaluates products based on material circularity and sustainability. |
Looking for these certifications ensures that the clothing you buy supports ethical and sustainable production.
Brands offering sustainable bamboo clothing
Examples of eco-conscious brands
Several brands prioritize sustainability in their bamboo clothing production. BAM Bamboo Clothing emphasizes supply chain transparency and has earned B Corp certification. Asquith avoids harmful chemicals, ensuring safer production methods. Carrot Banana Peach focuses on fair trade, providing fair wages and good working conditions for workers. These brands demonstrate how ethical practices can align with environmental goals.
How to research brand practices
To find sustainable bamboo clothing, research the brand’s values and certifications. Check if they disclose their production methods and sourcing practices. Look for transparency in their supply chain and whether they prioritize renewable resources. Reading customer reviews and third-party assessments can also help you make informed decisions.
Bamboo clothing offers significant environmental benefits, but its sustainability depends on how it is produced. Bamboo farming can enhance carbon fixation and reduce resource use, yet intensive farming may harm ecosystems. Similarly, while bamboo is a renewable crop, chemical-heavy viscose production raises concerns. Choosing clothing made with eco-friendly methods, like the lyocell process, ensures a lower environmental impact. Certifications such as OEKO-TEX and FSC help you identify responsibly made products. By prioritizing these factors, you can make informed choices and support sustainable practices.
FAQ
Why is bamboo clothing considered eco-friendly?
Bamboo grows quickly and requires fewer resources than other crops. It thrives without pesticides or fertilizers and uses less water than cotton. Its ability to absorb carbon dioxide also helps combat climate change. These factors make bamboo a sustainable choice when processed responsibly.
Why does bamboo viscose production harm the environment?
The viscose process uses toxic chemicals like carbon disulfide and caustic soda. These substances can pollute water and soil if not managed properly. Factories often lack sustainable waste practices, which increases the environmental impact. Choosing bamboo processed through safer methods reduces this harm.
How can you identify sustainable bamboo clothing?
Look for certifications like OEKO-TEX and FSC. These labels ensure the clothing is free from harmful substances and sourced responsibly. Research brands that disclose their production methods and prioritize eco-friendly practices. Supporting such brands helps promote sustainability.
Tip: Check for terms like “lyocell bamboo” or “bamboo linen” for greener options.
Is bamboo clothing better than cotton?
Bamboo uses less water and grows without pesticides, making it more sustainable than conventional cotton. However, organic cotton offers a greener alternative to regular cotton. Bamboo processed through eco-friendly methods, like the lyocell process, often has a lower environmental impact than both.
What are the best alternatives to bamboo clothing?
Hemp and lyocell are excellent alternatives. Hemp grows quickly, needs little water, and avoids pesticides. Lyocell uses a closed-loop process that recycles chemicals, reducing waste. Both fabrics have lower environmental impacts than chemically processed bamboo.
Note: Bamboo processed using the lyocell method competes well with these fabrics.
