When it comes to eco-friendly fabrics, bamboo fibre stands out as a sustainable and versatile material. Extracted from bamboo plants, it offers a soft texture, excellent breathability, and moisture-wicking properties. Unlike conventional cotton, bamboo requires less water and no pesticides, making it an environmentally friendly alternative in the textile industry.
Bamboo fibre is a natural textile material made from bamboo plants. It is known for being soft, breathable, moisture-wicking, and biodegradable. Due to its sustainability and versatility, it is widely used in clothing, home textiles, and eco-friendly products.
As the demand for sustainable materials grows, bamboo fibre is gaining popularity in various industries. The global bamboo fibre market is projected to reach $17.37 billion by 2034, reflecting its rising importance. But how exactly is bamboo fibre produced, and what makes it different from other natural fibres? Let’s explore its types, production methods, and key benefits.
Key Takeaways
- Bamboo fiber is good for the environment. It uses less water and no pesticides compared to cotton.
- Making bamboo fiber by machines is better for nature but takes more work and makes less fiber.
- Using chemicals to make bamboo fiber is faster and cheaper. However, it can hurt the environment if not handled well.
- Bamboo viscose feels soft and airy, great for clothes. But making it uses harmful chemicals.
- Bamboo lyocell is made in a safer way. It reuses chemicals, so it’s better for the planet.
- Natural bamboo fiber breaks down easily and is strong. But it costs more to make because it needs more work.
- Bamboo fiber naturally fights bacteria, so it’s perfect for clean and healthy products.
- Buying bamboo products made in eco-friendly ways helps the planet and supports fair work conditions.
How is Bamboo Fiber Made?

Bamboo fiber is created in two main ways: mechanical and chemical. Each way has its own steps, benefits, and challenges. Let’s explore both methods.
Mechanical Process
The mechanical method is natural and better for the environment. It breaks bamboo into fibers without harmful chemicals. Here’s how it’s done:
- Bamboo plants are harvested and crushed into small pieces.
- Natural enzymes soften the bamboo by breaking its cell walls.
- The soft fibers are combed and spun into yarn.
This process makes a fabric called bamboo linen. It feels like regular linen and is strong. But it takes a lot of work and costs more. It also produces less fiber than the chemical method.
Tip: Bamboo linen made this way is the most eco-friendly option.
Chemical Process
The chemical method is quicker and produces more fiber. It’s often used to make bamboo viscose or rayon. Here’s a simple breakdown of the steps:
- Bamboo is crushed into a pulp.
- The pulp is soaked in 20% sodium hydroxide (NaOH) at 20°C for three hours.
- The soda cellulose is dried for 24 hours.
- Carbon disulfide (CS2) is added, forming a jelly-like material.
- The jelly is dissolved in more NaOH to make viscose.
- The viscose is spun into fibers in a sulfuric acid (H2SO4) bath.
This method is cheaper and makes soft, flexible fabrics. But it can harm the environment and workers due to the chemicals used. Some companies reuse 99.5% of the chemicals in a closed-loop system, making it more eco-friendly.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Bamboo is crushed into pulp. |
| 2 | Pulp is soaked in 20% NaOH at 20°C for 3 hours. |
| 3 | Soda cellulose is dried for 24 hours. |
| 4 | CS2 is added to create a jelly-like compound. |
| 5 | NaOH dissolves the compound into a viscose solution. |
| 6 | Viscose is spun into fibers in an H2SO4 bath. |
Comparing Mechanical and Chemical Methods
Both methods have good and bad points. The mechanical method is eco-friendly and makes strong fabric. But it’s expensive and produces less fiber. The chemical method is faster and cheaper but uses harmful chemicals.
- Mechanical Process:
- Uses natural enzymes, so it’s eco-friendly.
- Makes strong, linen-like fabric.
- Costs more and takes more work.
- Chemical Process:
- Uses harmful chemicals like carbon disulfide.
- Makes soft, flexible fabrics.
- Can be eco-friendly with closed-loop systems.
When buying bamboo fiber products, choose ones made sustainably. It helps protect the planet.
What are the types of bamboo fiber?
Bamboo fiber comes in three main types. Each type has special features and is made differently. These types are Bamboo Viscose, Bamboo Lyocell, and Natural Bamboo Fiber.
Bamboo Viscose
Bamboo Viscose, also called bamboo rayon, is very common. It feels soft and smooth, making it great for clothes and home items. The chemical process used to make it allows for large-scale production. This helps meet the demand for eco-friendly fabrics.
This fiber is breathable and keeps moisture away. These qualities make it perfect for activewear and summer outfits. It also has natural antibacterial and UV protection benefits. However, making bamboo viscose uses chemicals like sodium hydroxide and carbon disulfide. These can harm the environment if not handled well. Some companies recycle 99.5% of these chemicals using closed-loop systems. This reduces waste and pollution.
Fun Fact: Bamboo viscose is softer than cotton and feels luxurious.
Bamboo Lyocell
Bamboo Lyocell is made using a greener process. Bamboo pulp is dissolved in an organic solvent, filtered, and spun into fibers. This method recycles 99% of the solvent, making it eco-friendly.
Here’s how bamboo lyocell is made:
- Bamboo is harvested and turned into pulp.
- The pulp is dissolved with an organic solvent.
- The solution is filtered and spun into fibers.
- The fibers are washed, dried, and woven into fabric.
Bamboo lyocell fabric is durable and easy to care for. It’s a great choice for those wanting sustainable and practical materials.
Natural Bamboo Fiber
Natural Bamboo Fiber is made through a mechanical process. This method uses natural enzymes to break bamboo into fibers. These fibers are combed and spun into yarn. The result is bamboo linen, which feels like regular linen but is more eco-friendly.
This fiber is biodegradable and breaks down without polluting. Bamboo grows fast and doesn’t need pesticides, making it renewable. However, the process takes more work and produces less fiber. This makes it costlier than chemical methods.
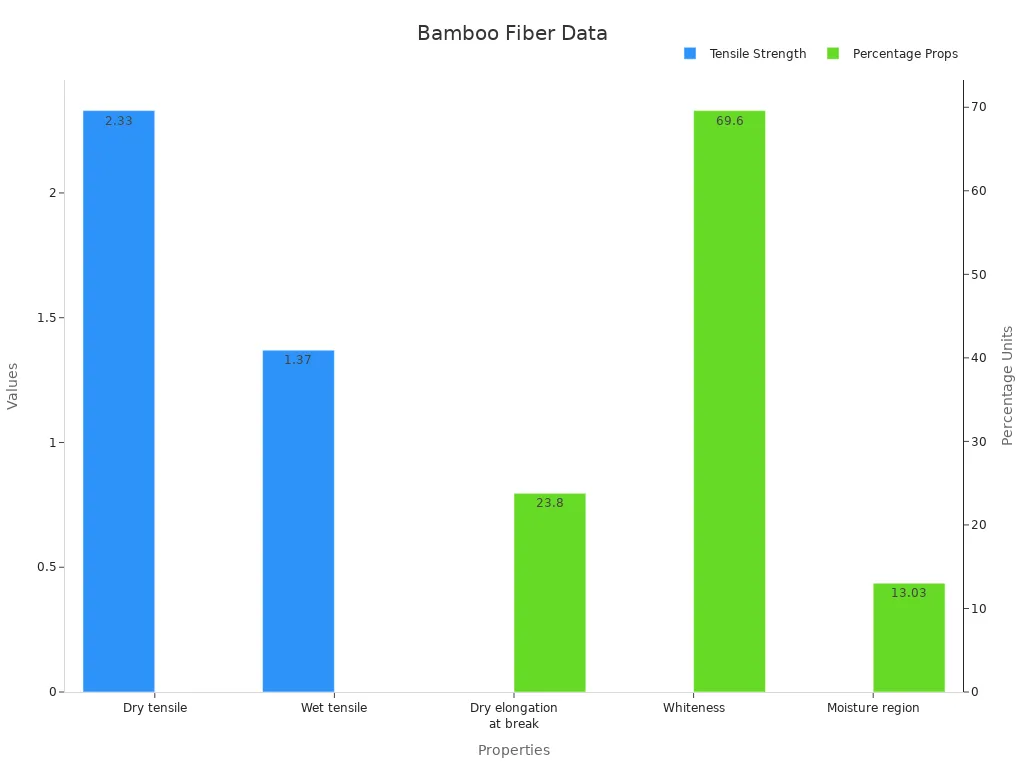
Note: Natural bamboo fiber is strong and absorbs moisture well. It’s durable and comfortable to use.
Each type of bamboo fiber has pros and cons. Whether you want softness, eco-friendliness, or strength, there’s a bamboo fiber for you.
What are the properties of bamboo fiber?
Physical Properties
Bamboo fiber has special physical traits that make it unique. It feels softer and smoother than cotton, giving it a fancy feel. Bamboo fabrics have tiny gaps in their structure. These gaps help absorb moisture and let air pass through. This keeps the fabric cool and comfy by wicking away sweat. That’s why it’s called the “Air Conditioning Dress.”
Studies show bamboo fibers are thicker than cotton ones. This makes them stronger and more durable. Bamboo also has natural antibacterial powers. It can fight bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus. These features make bamboo fiber great for clothes and other textiles.
Functional Properties
Bamboo fiber has many useful benefits that stand out. It handles moisture and temperature very well. Studies show bamboo fabrics absorb moisture and manage heat better. This makes them perfect for sportswear and summer outfits. But bamboo doesn’t always beat cotton or viscose in comfort. This shows bamboo isn’t always the top choice.
Bamboo also has natural antibacterial and UV-blocking abilities. These make it an eco-friendly fabric. Bamboo fiber fights bacteria and shields skin from harmful UV rays. Lab tests show bamboo keeps its antibacterial power even after processing. This makes it a good pick for hygiene-focused uses.
Key lab findings about bamboo fiber include:
- It fights bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus.
- It manages moisture and temperature very well.
- Mixing methods improves fiber quality.
Durability and Maintenance
Bamboo fiber is strong and lasts a long time. Products made from it are tested to ensure durability. Strength and function tests show bamboo fabrics resist damage. They are tough and can last for years.
Taking care of bamboo fabrics is easy. They are simple to wash and stay soft over time. Bamboo is also biodegradable, breaking down naturally without harm. Tests show bamboo resists mold and fungi, adding to its strength.
Here’s a table of tests done on bamboo fiber products:
| Test Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Chemical Composition Testing | Checks for harmful chemicals and toxins. |
| Physical and Mechanical Testing | Confirms strength, durability, and function of bamboo products. |
| Microbiological Testing | Tests for mold, fungi resistance, and effective antimicrobial treatments. |
Bamboo fiber is strong, useful, and easy to care for. These qualities make it a smart and eco-friendly choice for many uses.
What are the benefits of bamboo fiber?
Environmental Benefits
Bamboo fiber is great for the environment. Bamboo grows fast and needs little care. Unlike cotton, it doesn’t need pesticides or much water. This makes it a renewable and eco-friendly choice. Bamboo products help fight climate change and reduce waste. For example, they cut down plastic use and lower greenhouse gases. A study shows disposable bamboo items are 1.96 times better for the environment than average.
| Product Category | EBSP Score (Average) | Environmental Benefits Description |
|---|---|---|
| Disposable Bamboo Products | 1.96 times average | Helps reduce plastic waste and greenhouse gas emissions. |
| Bamboo Household Goods | N/A | N/A |
| Bamboo Packaging Products | N/A | N/A |
| Bamboo Engineering Materials | N/A | N/A |
| Bamboo Furniture Products | N/A | N/A |
| Bamboo Craft Products | N/A | N/A |
But large bamboo farms can harm nature and cause landslides. Picking bamboo from responsible sources helps avoid these problems.
Health Benefits
Bamboo fiber is good for your health too. It feels soft and airy on the skin. It’s also hypoallergenic, so it’s safe for sensitive skin. Bamboo has “bamboo Kun,” a natural substance that fights bacteria and fungi. This keeps fabrics fresh and odor-free.
Here are some health benefits of bamboo fiber:
- It’s soft and airy, making it comfy to wear.
- It’s hypoallergenic, great for people with allergies.
- It naturally fights bacteria and fungi, staying clean longer.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Softness | Bamboo fiber is softer than cotton, making it very comfy. |
| Moisture Absorption | Bamboo fabric absorbs moisture well and lets air flow. |
| Antibacterial Properties | Bamboo Kun gives it natural antibacterial and odor-fighting powers. |
| Hypoallergenic | It’s safe for sensitive skin and reduces allergic reactions. |
Bamboo’s health benefits make it perfect for baby clothes and bedding. It’s also popular for eco-friendly and health-focused products.
Economic Benefits
Bamboo fiber helps the economy in many ways. Bamboo grows quickly and is very useful. It creates jobs in farming, factories, and design. The bamboo industry supports fair pay and helps local communities. It also promotes sustainable growth and eco-friendly products.
Here’s how bamboo fiber boosts the economy:
- It gives women more chances to work in production.
- It supports green building and climate-friendly projects.
- It helps the economy grow with new, creative products.
Choosing bamboo fiber supports the planet and builds a fairer economy.
What is the environmental impact of bamboo fiber?
Positive Impacts
Making bamboo fiber has many environmental benefits. Bamboo grows fast and regrows on its own. It doesn’t need to be replanted after harvesting. This helps it absorb carbon and fight climate change. Unlike trees, which take many years to grow, bamboo is ready to harvest in 4-7 years. This quick growth gives farmers faster income and reduces the need to cut down forests. This helps stop deforestation.
The bamboo industry supports global sustainability goals. It helps with climate action, fair work, and eco-friendly living. For example, bamboo-based jobs give women more work opportunities. This promotes fairness and better lives for families. Bamboo factories often recycle up to 99% of chemicals. This lowers pollution and waste, making bamboo fiber a greener choice for buyers.
| Ecological Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Carbon Sequestration | Bamboo absorbs carbon dioxide and regrows without replanting. |
| Deforestation Reduction | Sustainable harvesting reduces the need for cutting down trees. |
| Faster Income for Farmers | Farmers earn money quicker than with traditional timber. |
| Supports SDGs | Helps with goals like climate action and fair work. |
Bamboo is useful for more than just fabrics. Its strength makes it great for building materials. This reduces the use of less eco-friendly resources. These benefits show why bamboo fiber is important for a sustainable future.
Concerns with Chemical Processing
Even with its benefits, making bamboo fiber using chemicals can harm the environment and health. The viscose process uses harmful chemicals like carbon disulfide, sodium hydroxide, and sulfuric acid. These chemicals can hurt workers and damage nature if not handled carefully.
- Carbon disulfide: Can harm the brain and cause organ damage.
- Sodium hydroxide: Can irritate skin and eyes, and may pollute water.
- Sulfuric acid: Can cause breathing problems and water pollution.
| Chemical | Effects on Workers | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon disulfide | Can harm the brain and cause serious health issues. | May damage ecosystems. |
| Sodium hydroxide | Causes skin and eye irritation. | Risk of polluting water sources. |
| Sulfuric acid | Can cause breathing problems. | May contaminate water supplies. |
Waste from poorly managed factories can pollute rivers and harm animals and people nearby. Workers exposed to these chemicals may face serious health problems. Some factories use closed-loop systems to recycle chemicals, but not all do. This shows the need for stricter rules and better practices in bamboo fiber production.
Shoppers can help by buying from brands that use safe and green methods. Choosing products made with bamboo lyocell supports eco-friendly and ethical production.
What are the applications of bamboo fiber?

Bamboo fiber is used in many industries because it’s versatile and eco-friendly. Let’s explore its main uses.
Clothing and Fashion
Bamboo fiber is popular in sustainable fashion. It’s soft and breathable, making it great for casual clothes, sportswear, and underwear. Many brands use bamboo fabrics to create stylish and eco-friendly clothing. Its natural antibacterial and moisture-wicking features make it perfect for workout gear, keeping you fresh and comfy.
- Why Choose Bamboo for Clothes?
- It’s gentle on sensitive skin.
- It keeps you cool in summer and warm in winter.
- It breaks down naturally, helping the environment.
Fun Fact: Bamboo clothes are fashionable and reduce the fashion industry’s environmental impact.
Home Textiles
Bamboo fiber is changing home textiles by offering a greener option. It’s used in bedding, towels, and carpets. Its softness and hypoallergenic qualities make it ideal for items that touch the skin. Bamboo sheets are smooth and breathable, helping you sleep better.
The demand for bamboo home products is growing fast. Items like curtains and furniture covers made from bamboo fiber look stylish and support eco-friendly living. Studies show home décor is a big market for bamboo fiber due to rising interest in sustainable designs.
- Common Bamboo Home Items:
- Bedsheets and pillowcases
- Towels and bathrobes
- Carpets and rugs
Tip: Want an eco-friendly home? Start with bamboo textiles.
Industrial and Specialty Uses
Bamboo fiber is also used in industries for its strength and durability. It’s found in car interiors, biocomposites, and filtration materials. These uses show how bamboo fiber works well in high-performance products.
Here are some industrial uses of bamboo fiber:
| Application Area | Features and Benefits | Examples of Use |
|---|---|---|
| High-performance textiles | Strong, durable, stable, and antibacterial | Sanitary napkins, masks, mattresses |
| UV-resistant products | Blocks UV rays, safe for sensitive skin | Clothes for pregnant women and kids |
| Household items | Flexible, fine, eco-friendly, and visually appealing | TV covers, wallpaper, sofa slipcovers |
Bamboo fiber inspires new ideas. It’s used in medical bandages, car parts, and more. Its applications grow as people seek sustainable materials.
Note: Buying bamboo-based industrial products helps the planet and reduces the use of non-renewable resources.
Bamboo fiber is a sustainable and useful material. It grows quickly and needs little water or pesticides, making it eco-friendly. Its softness, breathability, and ability to fight bacteria make it great for clothes and home items. But, large farms and chemical processing can cause problems if not managed well. Choosing bamboo products from responsible sources helps protect the environment. With its special features and many uses, bamboo fiber is important for creating eco-friendly fabrics.
FAQ
Is bamboo fiber really eco-friendly?
Yes, bamboo fiber is eco-friendly if made responsibly. Bamboo grows fast without needing pesticides or fertilizers. But chemical processing can harm nature. Choosing products made with closed-loop systems is a greener choice.
What are the disadvantages of bamboo fiber?
Bamboo fiber has some downsides. Chemical processing can hurt workers and the environment. Natural bamboo fiber takes more time and costs more to make. Some bamboo fabrics may shrink or wrinkle easily.
How do you care for bamboo fiber clothing?
Wash bamboo clothes in cold water on a gentle cycle. Don’t use bleach or strong detergents. Air-dry them or use low heat in the dryer. This keeps the fabric soft and lasting longer.
Does bamboo fiber shrink after washing?
Yes, bamboo fiber might shrink a little. Washing in hot water or drying on high heat can cause this. Use cold water and low heat to avoid shrinking.
Is bamboo fiber safe for sensitive skin?
Yes! Bamboo fiber is soft and hypoallergenic. It’s gentle on sensitive skin. Its natural antibacterial properties also keep it fresh and odor-free.
What makes bamboo fiber better than cotton?
Bamboo fiber absorbs moisture better and feels softer than cotton. It’s more eco-friendly because bamboo grows faster and needs less water. But some cotton fabrics may last longer.
Can bamboo fiber be recycled?
Yes, bamboo fiber can be recycled, especially in textiles. Some companies reuse old bamboo fabrics to make new items. This reduces waste and supports sustainability.
Why is bamboo fiber called breathable?
Bamboo fiber has tiny holes that let air flow through. This keeps the fabric cool and comfy, making it great for summer clothes and activewear.
